How to spot climate misinformation and disinformation, and counter both
Communication expert Kathryn Bonner understands the environmental crisis is a battle of hearts and minds, with lobbyists and campaigners on the frontline.
As someone who has been closely following the evolving landscape of climate communications, I am acutely aware of the challenges that lie ahead. At ACT Climate Labs, we are on a mission to transform the way we approach talking about climate with people who are not activists or climate deniers. We call these people ‘Persuadables’ as they are being targeted by bad actors with confusing and malicious disinformation, which is, in turn, undermines the consensus around climate action, human rights, and other progressive causes.
The UK has made international commitments to stay within 2C, preferably 1.5C, of temperature rise above pre-industrial levels. To honour this, the UK needs to decarbonise rapidly – known in some circles as ‘climate action’. However, climate change disinformation and misinformation are a major threat to success. They distort public perception of climate science and the necessary paths to decarbonisation.
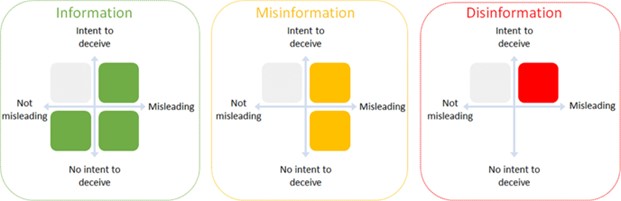
What is the difference between climate misinformation and disinformation?
The difference is intent. Those sharing or creating climate misinformation may not realise the information is false. However, disinformation spreaders share false information deliberately.
What is climate misinformation?
At ACT Climate Labs we use the same definition as Climate Action Against Disinformation (CAAD) – a coalition of experts in climate and disinformation.
Climate misinformation includes any deceptive or misleading content that undermines the existence or severity of climate change, our contribution to it or the need for corresponding action. As well as climate change greenwashing, it includes the act of exaggerating or lying about decarbonisation initiatives. Anything outside of this definition could be termed adversarial content, or misleading, but isn’t necessarily misinformation.
Who creates and shares climate misinformation, and why?
Given the scale and urgency of climate change, we could question why anyone would want to create environmental disinformation or share misinformation in the first place. Experts have narrowed their answer down to two main reasons:
- Extending the life of fossil fuels and business-as-usual profits.
- Earning revenue, clout or support for related causes by exploiting the attention economy. That is, exploiting the tendency to gain more attention online and offline by spreading highly emotional or controversial content.
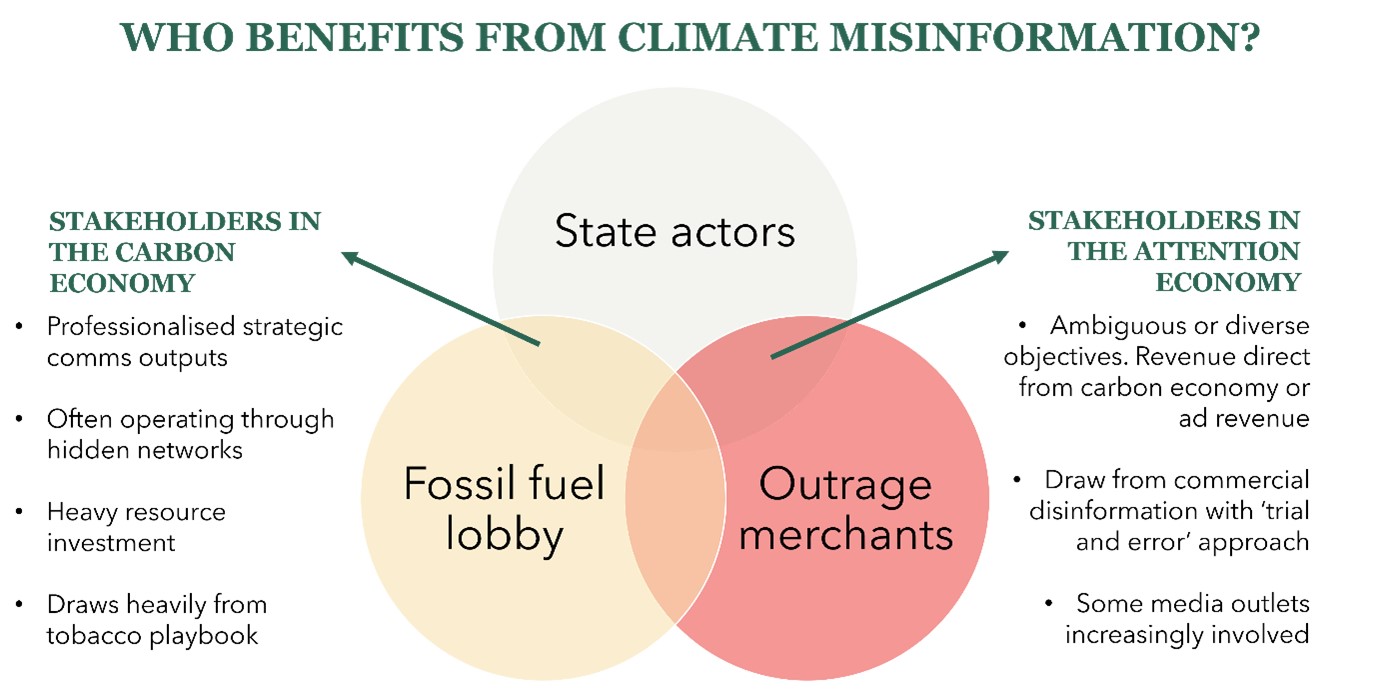
Who benefits from climate misinformation? Diagram adapted by ACT Climate Labs from CAAD coalition.
Climate misinformation is fuelled typically by a diverse range of sources: companies, governments, politicians, media outlets, organised groups online and offline, as well as online ‘chancers’ who just want to make a bit of ad revenue.
There are roughly 69% of Brits who are not climate activists not deniers. They are a diverse group we refer to as the ‘Persuadables’ – not yet ‘sold’ on various aspects of climate action. Climate misinformation is most damaging if it convinces this group.
The different types of climate misinformation
There are various taxonomies of climate misinformation out there. Yet when it comes to Persuadables, we think of four broad categories: 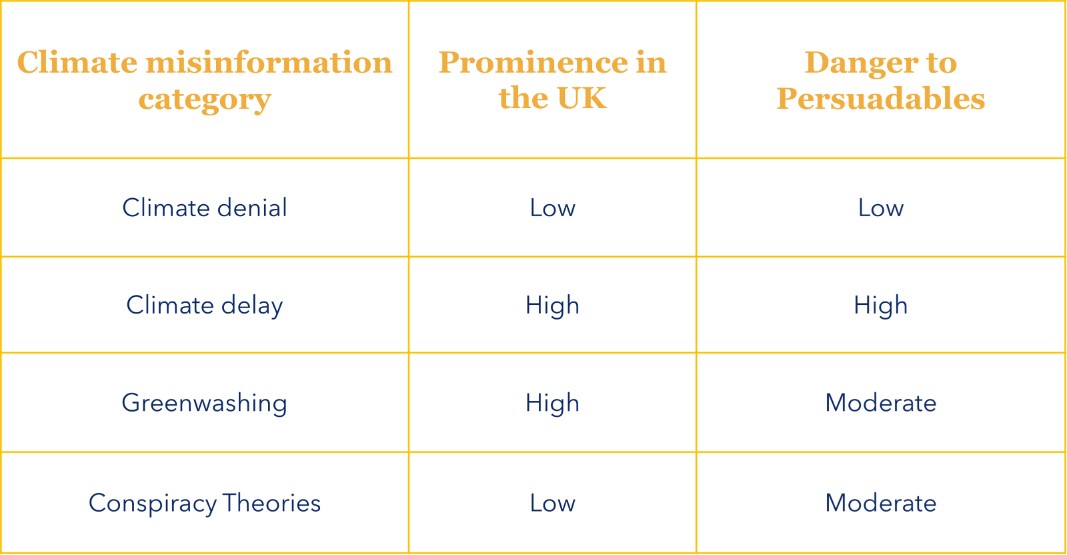
- Climate Denial
When people hear the term ‘climate misinformation’, they usually think of denial first. Climate denial includes narratives that deny the existence of climate change, humans’ contribution to it, or the severity of its impacts.
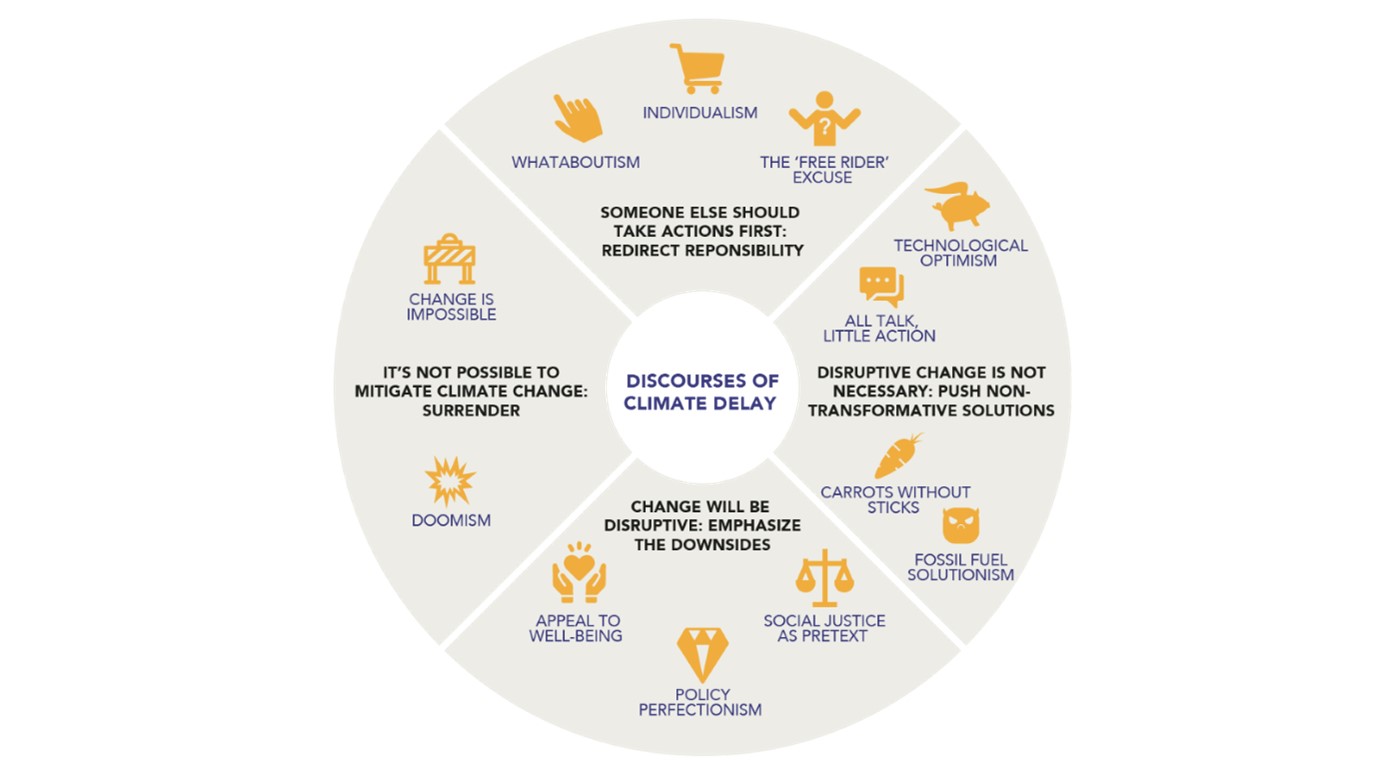
- Climate delay
Delay messaging usually accepts the existence of human-induced climate change but seeks to block or slow down measures to decarbonise. For this reason, it is often focused on specific policies and technologies. Responding to this kind of misinformation can be tricky, because the knowledge base covers a wide range of different policies, technologies and current events. Based on analysis, it is by far the most common and effective form of climate misinformation seen in the UK.
- Greenwashing
Greenwashing is presenting your company or product as more environmentally friendly than it really is. This is technically a form of climate delay but it stands out as its own issue due to multi-million-dollar marketing and lobbying budgets committed to it – especially from the fossil fuel industry.
Research shows that while members of the public are usually good at spotting misleading information on products, we are susceptible to misleading ideas. We are more likely to believe promotions that cater to our intrinsic values, or that adopt ‘executional greenwashing’. These often use images and sounds of nature, clean energy and happy communities, rather than specific claims about products themselves.
- Conspiracy
People that believe conspiracy theories are unfairly branded as fanatics. In fact, up to 1 in 3 Britons may already believe some kind of conspiracy; and at the height of its popularity, 1 in 4 believed some kind of QAnon conspiracy. When it comes to climate conspiracy theories, the most popular is the age-hold ‘climate change is a hoax’ narrative. This is believed by between 7 and 8% of Brits.
As the impact of climate change becomes more visible in the UK, the risk is that Persuadables will turn to alternative explanations not based in climate science to cope. Recent studies on TikTok and Instagram clearly outline the risk.
What can we do about climate misinformation?
Communications and campaigning professionals hold a lot of power. With the right frames and tactics, we can:
- Promote positive, truthful stories at scale: Recognising that conspiracies stem from confusion, distrust, and a feeling of anxiety and lack of control; we can counter-message with advertising campaigns aimed at ‘Persuadables’ with positive, truthful stories about climate at a regional, national or international scale. Reframe action for decarbonisation in a way that is attractive to Persuadables.
- Embrace mass modern media: leveraging advertising to ensure mass reach of campaign messages, that inoculate those most at risk of misinformation. Helping scale campaigns quickly and avoid being distracted by misinformation traps. Inoculate Persuadables against climate misinformation before they see it, preferably through a combination of organic and paid media.
- Combining fact-based and emotional messaging: NGOs, for example, often rely on scientifically backed information and facts in their communication efforts. Providing verifiable data is an effective countermeasure against disinformation, but it’s not enough to make it stick. At ACT, we use techniques such as Fact, Myth, Fallacy to effectively reverse belief in misinformation. This approach can help shift public opinion and foster greater support for initiatives related to climate action.
We stand at a critical juncture in our journey towards a sustainable future. It’s time to recognise the indispensable role of advertising in reaching those who can be persuaded by evidence-based messaging. With 2billion people poised to make critical decisions at the polls in the coming 12 months, the need for accurate information has never been greater. The time to act is now, or risk jeopardising our shared vision of a more balanced and equitable future.
More features and opinion:
https://environmentjournal.online/editors-pick/englishwoman-who-bought-a-mountain-and-planted-250000-trees/
https://environmentjournal.online/headlines/sustainable-supermarket-choices/
https://environmentjournal.online/headlines/biodiversity-net-gain-active-policy/
Images: Mika Baumeister (top)